Evidence: Islam is Truth
The Earths Atmosphere
The Qur`an on Human Embryonic Development
Qur`an on the Origin of the Universe
Qur`an on Mountain
The Earth`s Atmosphere:
Description: Modern science has discovered facts about the atmosphere mentioned in the Quran over 1400 years ago.
“By the sky which returns.” (Quran 86:11)
“[He] who made for you the earth a bed [spread out] and the sky a ceiling…” (Quran 2:22)
In the first verse God swears by the sky[1] and its function of ‘returning’ without specifying what it ‘returns.’ In Islamic doctrine, a divine oath signifies the magnitude of importance of a special relation to the Creator, and manifests His majesty and the supreme Truth in a special way.
The second verse describes the Divine Act that made the sky a ‘ceiling’ for the dwellers of earth.
Let us see what modern atmospheric science has to say about the role and function of the sky.
The atmosphere is a word which denotes all the air surrounding the earth, from the ground all the way up to the edge from which space starts. The atmosphere is composed of several layers, each defined because of the various phenomena which occur within the layer.
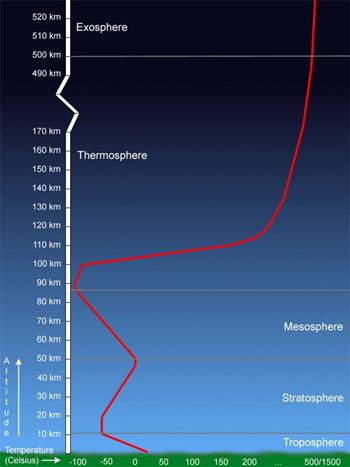
This image shows the average temperature profile through the Earth’s atmosphere. Temperatures in the thermosphere are very sensitive to solar activity and can vary from 500°C to 1500°C. Source: Windows to the Universe, (http://www.windows.ucar.edu), the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR). ©1995-1999, 2000 The Regents of the University of Michigan; ©2000-04 University Corporation for Atmospheric Research.
Rain, for one, is ‘returned’ to Earth by the clouds in the atmosphere. Explaining the hydrologic cycle, Encyclopedia Britannica writes:
“Water evaporates from both the aquatic and terrestrial environments as it is heated by the Sun’s energy. The rates of evaporation and precipitation depend on solar energy, as do the patterns of circulation of moisture in the air and currents in the ocean. Evaporation exceeds precipitation over the oceans, and this water vapor is transported by the wind over land, where it returns to the land through precipitation.”[2]
Not only does the atmosphere return what was on the surface back to the surface, but it reflects back into space that which might damage the flora and fauna the earth sustains, such as excessive radiant heat. In the 1990’s, collaborations between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS) of Japan resulted in the International Solar-Terrestrial Physics (ISTP) Science Initiative. Polar, Wind and Geotail are a part of this initiative, combining resources and scientific communities to obtain coordinated, simultaneous investigations of the Sun-Earth space environment over an extended period of time. They have an excellent explanation of how the atmosphere returns solar heat to space.[3]
Besides ‘returning’ rain, heat and radio waves, the atmosphere protects us like a ceiling above our heads by filtering out deadly cosmic rays, powerful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun, and even meteorites on collision course with Earth.[4]
Pennsylvania State Public Broadcasting tells us:
“The sunlight that we can see represents one group of wavelengths, visible light. Other wavelengths emitted by the sun include x-rays and ultraviolet radiation. X-rays and some ultraviolet light waves are absorbed high in Earth’s atmosphere. They heat the thin layer of gas there to very high temperatures. Ultraviolet light waves are the rays that can cause sunburn. Most ultraviolet light waves are absorbed by a thicker layer of gas closer to Earth called the ozone layer. By soaking up the deadly ultraviolet and x-rays, the atmosphere acts as a protective shield around the planet. Like a giant thermal blanket, the atmosphere also keeps temperatures from getting too hot or too cold. In addition, the atmosphere also protects us from constant bombardment by meteoroids, bits of rock and dust that travel at high speeds throughout the solar system. The falling stars we see at night are not stars at all; they are actually meteoroids burning up in our atmosphere due to the extreme heating they undergo.”[5]

This is an image of Earth’s polar stratospheric clouds. These clouds are involved in the creation of Earth’s ozone hole. Source: Windows to the Universe, (http://www.windows.ucar.edu/) at the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR). ©1995-1999, 2000 The Regents of the University of Michigan; ©2000-04 University Corporation for Atmospheric Research.
Encyclopedia Britannica, describing the role of Stratosphere, tells us about its protective role in absorbing dangerous ultraviolet radiation:
“In the upper stratospheric regions, absorption of ultraviolet light from the Sun breaks down oxygen molecules; recombination of oxygen atoms with O2 molecules into ozone (O3) creates the ozone layer, which shields the lower ecosphere from harmful short-wavelength radiation…More disturbing, however, is the discovery of a growing depletion of ozone over temperate latitudes, where a large percentage of the world’s population resides, since the ozone layer serves as a shield against ultraviolet radiation, which has been found to cause skin cancer.”[6]
The mesosphere is the layer in which many meteors burn up while entering the Earth’s atmosphere. Imagine a baseball zipping along at 30,000 miles per hour. That’s how big and fast many meteors are. When they plow through the atmosphere, meteors are heated to more than 3000 degrees Fahrenheit, and they glow. A meteor compresses air in front of it. The air heats up, in turn heating the meteor.[7]

This is an image which shows the Earth and its atmosphere. The mesosphere would be the dark blue edge located on the far top of the image underneath the back.
(Image courtesy of NASA)
Earth is surrounded by a magnetic force field - a bubble in space called “the magnetosphere” tens of thousands of miles wide. The magnetosphere acts as a shield that protects us from solar storms. However, according to new observations from NASA’s IMAGE spacecraft and the joint NASA/European Space Agency Cluster satellites, immense cracks sometimes develop in Earth’s magnetosphere and remain open for hours. This allows the solar wind to gush through and power stormy space weather. Fortunately, these cracks do not expose Earth’s surface to the solar wind. Our atmosphere protects us, even when our magnetic field does not.[8]
An artist’s rendition of NASA’s IMAGE satellite flying through a ‘crack’ in Earth’s magnetic field.
How would it be possible for a fourteenth century desert dweller to describe the sky in a manner so precise that only recent scientific discoveries have confirmed it? The only way is if he received revelation from the Creator of the sky.
Footnotes: [1] Al-Samaa’, the Arabic word translated here as ‘sky’ includes earth’s atmosphere as indicated by the verse 2:164.[2] ”Biosphere.” Encyclopedia Britannica from Encyclopedia Britannica Premium Service.
(http://www.britannica.com/eb/article?tocId=70872)[3] (http://www-spof.gsfc.nasa.gov/stargaze/Sweather1.htm)[4] Atmospheric, Climate & Environment Information Programme of the Manchester Metropolitan University at (http://www.ace.mmu.ac.uk/eae/Atmosphere/atmosphere.html)[5] (http://www.witn.psu.edu/articles/article.phtml?article_id=255&show_id=44)[6] “Earth.” Encyclopedia Britannica from Encyclopedia Britannica Premium Service.
(http://www.britannica.com/eb/article?tocId=54196)
[7] (http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/solarsystem/meteors-ez.html)[8] (http://www.firstscience.com/SITE/ARTICLES/magnetosphere.asp)
-------------------------------------------------------------------
|
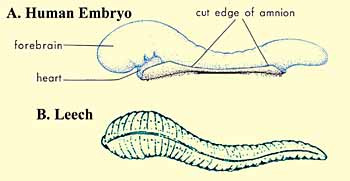
The Qur`an on Human Embryonic Development: “We created man from an extract of clay. Then We made him as a drop in a place of settlement, firmly fixed. Then We made the drop into an alaqah (leech, suspended thing, and blood clot), then We made the alaqah into a mudghah (chewed substance)…” (Quran 23:12-14 In comparing a leech to an embryo in the alaqah stage, we find similarity between the two[1] as we can see in figure 1. Also, the embryo at this stage obtains nourishment from the blood of the mother, similar to the leech, which feeds on the blood of others.[2]
Figure 1: Drawings illustrating the similarities in appearance between a leech and a human embryo at the alaqah stage. (Leech drawing from Human Development as Described in the Quran and Sunnah, Moore and others, p. 37, modified from Integrated Principles of Zoology, Hickman and others. Embryo drawing from The Developing Human, Moore and Persaud, 5th ed., p. 73.) The second meaning of the word alaqah is “suspended thing.” This is what we can see in figures 2 and 3, the suspension of the embryo, during the alaqah stage, in the womb of the mother.
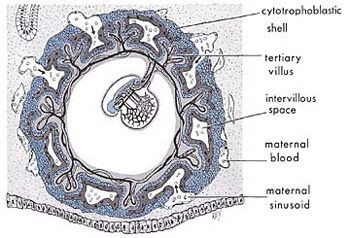
Figure 2: We can see in this diagram the suspension of an embryo during the alaqah stage in the womb (uterus) of the mother. (The Developing Human, Moore and Persaud, 5th ed., p. 66.)
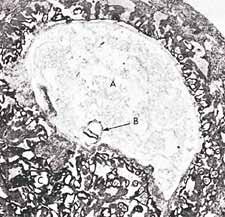
Figure 3: In this photomicrograph, we can see the suspension of an embryo (marked B) during the alaqah stage (about 15 days old) in the womb of the mother. The actual size of the embryo is about 0.6 mm. (The Developing Human, Moore, 3rd ed., p. 66, from Histology, Leeson and Leeson.) The third meaning of the word alaqah is “blood clot.” We find that the external appearance of the embryo and its sacs during the alaqah stage is similar to that of a blood clot. This is due to the presence of relatively large amounts of blood present in the embryo during this stage[3] (see figure 4). Also during this stage, the blood in the embryo does not circulate until the end of the third week.[4] Thus, the embryo at this stage is like a clot of blood.
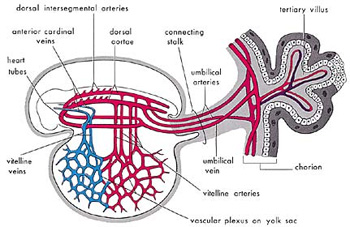
Figure 4: Diagram of the primitive cardiovascular system in an embryo during the alaqah stage. The external appearance of the embryo and its sacs is similar to that of a blood clot, due to the presence of relatively large amounts of blood present in the embryo. (The Developing Human, Moore, 5th ed., p. 65.) So the three meanings of the word alaqah correspond accurately to the descriptions of the embryo at the alaqah stage. The next stage mentioned in the verse is the mudghah stage. The Arabic word mudghah means “chewed substance.” If one were to take a piece of gum and chew it in his or her mouth and then compare it with an embryo at the mudghah stage, we would conclude that the embryo at the mudghah stage acquires the appearance of a chewed substance. This is because of the somites at the back of the embryo that “somewhat resemble teethmarks in a chewed substance.”[5] (see figures 5 and 6).
Figure 5: Photograph of an embryo at the mudghah stage (28 days old). The embryo at this stage acquires the appearance of a chewed substance, because the somites at the back of the embryo somewhat resemble teeth marks in a chewed substance. The actual size of the embryo is 4 mm. (The Developing Human, Moore and Persaud, 5th ed., p. 82, from Professor Hideo Nishimura, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan.)
Figure 6: When comparing the appearance of an embryo at the mudghah stage with a piece of gum that has been chewed, we find similarity between the two. A) Drawing of an embryo at the mudghah stage. We can see here the somites at the back of the embryo that look like teeth marks. (The Developing Human, Moore and Persaud, 5th ed., p. 79.) B) Photograph of a piece of gum that has been chewed. How could Muhammad, may the mercy and blessings of God be upon him, have possibly known all this 1400 years ago, when scientists have only recently discovered this using advanced equipment and powerful microscopes which did not exist at that time? Hamm and Leeuwenhoek were the first scientists to observe human sperm cells (spermatozoa) using an improved microscope in 1677 (more than 1000 years after Muhammad). They mistakenly thought that the sperm cell contained a miniature preformed human being that grew when it was deposited in the female genital tract.[6] Professor Emeritus Keith L. Moore[7] is one of the world’s most prominent scientists in the fields of anatomy and embryology and is the author of the book entitled The Developing Human, which has been translated into eight languages. This book is a scientific reference work and was chosen by a special committee in the United States as the best book authored by one person. Dr. Keith Moore is Professor Emeritus of Anatomy and Cell Biology at the University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada. There, he was Associate Dean of Basic Sciences at the Faculty of Medicine and for 8 years was the Chairman of the Department of Anatomy. In 1984, he received the most distinguished award presented in the field of anatomy in Canada, the J.C.B. Grant Award from the Canadian Association of Anatomists. He has directed many international associations, such as the Canadian and American Association of Anatomists and the Council of the Union of Biological Sciences. In 1981, during the Seventh Medical Conference in Dammam, Saudi Arabia, Professor Moore said: “It has been a great pleasure for me to help clarify statements in the Quran about human development. It is clear to me that these statements must have come to Muhammad from God, because almost all of this knowledge was not discovered until many centuries later. This proves to me that Muhammad must have been a messenger of God.”[8] (To view the RealPlayer video of this comment click here). Consequently, Professor Moore was asked the following question: “Does this mean that you believe that the Quran is the word of God?” He replied: “I find no difficulty in accepting this.”[9] During one conference, Professor Moore stated: “....Because the staging of human embryos is complex, owing to the continuous process of change during development, it is proposed that a new system of classification could be developed using the terms mentioned in the Quran and Sunnah (what Muhammad, may the mercy and blessings of God be upon him, said, did, or approved of). The proposed system is simple, comprehensive, and conforms with present embryological knowledge. The intensive studies of the Quran and hadeeth (reliably transmitted reports by the Prophet Muhammad’s companions of what he said, did, or approved of) in the last four years have revealed a system for classifying human embryos that is amazing since it was recorded in the seventh century A.D. Although Aristotle, the founder of the science of embryology, realized that chick embryos developed in stages from his studies of hen’s eggs in the fourth century B.C., he did not give any details about these stages. As far as it is known from the history of embryology, little was known about the staging and classification of human embryos until the twentieth century. For this reason, the descriptions of the human embryo in the Quran cannot be based on scientific knowledge in the seventh century. The only reasonable conclusion is: these descriptions were revealed to Muhammad from God. He could not have known such details because he was an illiterate man with absolutely no scientific training.”[10] (View the RealPlayer video of this comment). Footnotes: [1] The Developing Human, Moore and Persaud, 5th ed., p. 8.[2] Human Development as Described in the Quran and Sunnah, Moore and others, p. 36.[3] Human Development as Described in the Quran and Sunnah, Moore and others, pp. 37-38.[4] The Developing Human, Moore and Persaud, 5th ed., p. 65.[5] The Developing Human, Moore and Persaud, 5th ed., p. 8.6] The Developing Human, Moore and Persaud, 5th ed., p. 9.7] Note: The occupations of all the scientists mentioned in this web site were last updated in 1997.8] The reference for this saying is This is the Truth (videotape). For a copy of this videotape, please visit www.islam-guide.com/truth.htm9] This is the Truth (videotape).10] This is the Truth (videotape). For a copy, see footnote no. 9. |
The Qur`an on the Origin of the Universe
Description: A Scientific and Quranic explanation about the creation of the universe
 The science of modern cosmology, observational and theoretical, clearly indicates that, at one point in time, the whole universe was nothing but a cloud of ‘smoke’ (i.e. an opaque highly dense and hot gaseous composition).[1] This is one of the undisputed principles of standard modern cosmology. Scientists now can observe new stars forming out of the remnants of that ‘smoke’ (see figures 1 and 2).
The science of modern cosmology, observational and theoretical, clearly indicates that, at one point in time, the whole universe was nothing but a cloud of ‘smoke’ (i.e. an opaque highly dense and hot gaseous composition).[1] This is one of the undisputed principles of standard modern cosmology. Scientists now can observe new stars forming out of the remnants of that ‘smoke’ (see figures 1 and 2).

Figure 1: A new star forming out of a cloud of gas and dust (nebula), which is one of the remnants of the ‘smoke’ that was the origin of the whole universe. (The Space Atlas, Heather and Henbest, p. 50.)

Figure 2: The Lagoon nebula is a cloud of gas and dust, about 60 light years in diameter. It is excited by the ultraviolet radiation of the hot stars that have recently formed within its bulk. (Horizons, Exploring the Universe, Seeds, plate 9, from Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc.)
The illuminating stars we see at night were, just as was the whole universe, in that ‘smoke’ material. God has said in the Quran:
“Then He turned to the heaven when it was smoke...” (Quran 41:11)
Because the earth and the heavens above (the sun, the moon, stars, planets, galaxies, etc.) have been formed from this same ‘smoke,’ we conclude that the earth and the heavens were one connected entity. Then out of this homogeneous ‘smoke,’ they formed and separated from each other. God has said in the Quran:
“Have not those who disbelieved known that the heavens and the earth were one connected entity, then We separated them?...” (Quran 21:30)
Dr. Alfred Kroner is one of the world’s renowned geologists. He is Professor of Geology and the Chairman of the Department of Geology at the Institute of Geosciences, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz, Germany. He said: “Thinking where Muhammad came from . . . I think it is almost impossible that he could have known about things like the common origin of the universe, because scientists have only found out within the last few years, with very complicated and advanced technological methods, that this is the case.”[2] (To view the RealPlayer video of this comment click here). Also he said: “Somebody who did not know something about nuclear physics fourteen hundred years ago could not, I think, be in a position to find out from his own mind, for instance, that the earth and the heavens had the same origin.”[3] (View the RealPlayer video of this comment).
Footnotes: [1] The First Three Minutes, a Modern View of the Origin of the Universe, Weinberg, pp. 94-105.[2] The reference for this saying is This is the Truth (videotape). For a copy of this videotape, please visit this page.[3] This is the Truth (videotape).
---------------------------------------------------------
The Qur`an on Mountain:
Description: Both the Quran and science agree to the structural makeup of mountains and the role they play in maintaining the stability of the Earth.
 A book entitled Earth is a basic reference textbook in many universities around the world. One of its two authors is Professor Emeritus Frank Press. He was the Science Advisor to former US President Jimmy Carter, and for 12 years was the President of the National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC. His book says that mountains have underlying roots.[1] These roots are deeply embedded in the ground, thus, mountains have a shape like a peg (see figures 1, 2, and 3).
A book entitled Earth is a basic reference textbook in many universities around the world. One of its two authors is Professor Emeritus Frank Press. He was the Science Advisor to former US President Jimmy Carter, and for 12 years was the President of the National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC. His book says that mountains have underlying roots.[1] These roots are deeply embedded in the ground, thus, mountains have a shape like a peg (see figures 1, 2, and 3).
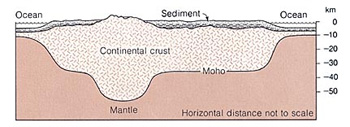
Figure 1: Mountains have deep roots under the surface of the ground. (Earth, Press and Siever, p. 413.)
Figure 2: Schematic section. The mountains, like pegs, have deep roots embedded in the ground. (Anatomy of the Earth, Cailleux, p. 220.)
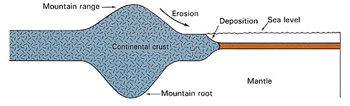
Figure 3: Another illustration shows how the mountains are peg-like in shape, due to their deep roots. (Earth Science, Tarbuck and Lutgens, p. 158.)
This is how the Quran has described mountains. God has said in the Quran:
“Have We not made the earth as a bed, and the mountains as pegs?” (Quran 78:6-7)
Modern earth sciences have proven that mountains have deep roots under the surface of the ground (see figure 3) and that these roots can reach several times their elevations above the surface of the ground.[2] So the most suitable word to describe mountains on the basis of this information is the word ‘peg,’ since most of a properly set peg is hidden under the surface of the ground. The history of science tells us that the theory of mountains having deep roots was introduced only in the latter half of the nineteenth century.[3]
Mountains also play an important role in stabilizing the crust of the earth.[4] They hinder the shaking of the earth. God has said in the Quran:
“And He has set firm mountains in the earth so that it would not shake with you...” (Quran 16:15)
Likewise, the modern theory of plate tectonics holds that mountains work as stabilizers for the earth. This knowledge about the role of mountains as stabilizers for the earth has just begun to be understood in the framework of plate tectonics since the late 1960’s.[5]
Could anyone during the time of the Prophet Muhammad have known of the true shape of mountains? Could anyone imagine that the solid massive mountain which he sees before him actually extends deep into the earth and has a root, as scientists assert? A large number of books of geology, when discussing mountains, only describe that part which is above the surface of the earth. This is because these books were not written by specialists in geology. However, modern geology has confirmed the truth of the Quranic verses.
Could anyone imagine that the solid massive mountain which he sees before him actually extends deep into the earth and has a root, as scientists assert? A large number of books of geology, when discussing mountains, only describe that part which is above the surface of the earth. This is because these books were not written by specialists in geology. However, modern geology has confirmed the truth of the Quranic verses.
Footnotes: [1] Earth, Press and Siever, p. 435. Also see Earth Science, Tarbuck and Lutgens, p. 157.[2] The Geological Concept of Mountains in the Quran, El-Naggar, p. 5.[3] The Geological Concept of Mountains in the Quran, p. 5.[4] The Geological Concept of Mountains in the Quran, pp. 44-45.[5] The Geological Concept of Mountains in the Quran, p. 5.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HADITHS ------>O Allah, You are my Lord, none has the right to be worshipped except You, You have created me and I am your servant and I abide to Your covenant and promise as best as I can, I seek refuge in You from the evil of what I have done (wrong), I acknowledge Your favor upon me and I acknowledge my sin, so forgive me, for none forgives sins except You”. [Reported by Al-Bukhari]. ----->“O Ever Living, O self-Subsisting and supporter of all, by Your Mercy I seek help, rectify for me all of my affairs and do not leave me depend on myself, even for the blink of an eye”. [Reported by Tirmidhi ----->Abu Hurairah (May Allah be pleased with him) reported: The Messenger of Allah Sall-Allahu alayhi wa sallam said, "There are two statements that are light for the tongue to remember, heavy in the Scales and are dear to the Merciful: `Subhan-Allahi wa bihamdihi, Subhan-Allahil- Azim [Glory be to Allah and His is the praise, (and) Allah, the Greatest is free from imperfection)'.'' [Al-Bukhari and Muslim]. ----->Abu Hurairah (May Allah be pleased with him) reported: The Messenger of Allah (PBUH) said, "He who calls others to follow the Right Guidance will have a reward equal to the reward of those who follow him, without their reward being diminished in any respect on that account.'' [Muslim]. QURAN VERSES ----->My Lord! I seek refuge with You from the whisperings (suggestions) of the Shayatin (devils). And I seek refuge with You, My Lord! lest they may attend (or come near) me." (23/97-98) ----->If there were, in the heavens and the earth, other gods besides Allâh, there would have been ruin in both! But glory to Allâh, the Rabb of the Throne: (High is He) above what they attribute to Him." (21: 22) ----->And we have not sent you ( O Muhammad ) except as a giver of glad tidings and a warner to all mankind, but most of them know not." (Quran 34:28)--> And whatever the Messenger gives you, take it, and whatever he forbids you, leave it. And fear Allah: truly Allah is severe in punishment. " [Qur'an 59:7] ----->Allah says: "Every soul shall have the taste of death: And only on the Day of Judgment shall you be paid your full recompense. Only he who is saved far from the Fire and admitted to the Garden will have succeeded: For the life of this world is but goods and chattels of deception." [3:185]. ----->Our Lord! Give us in this world that which is good and in the Hereafter that which is good, and save us from the torment of the Fire!" (The Holy Qur'an 2:201) ----->All the praises and thanks be to Allah, Who has guided us to this, and never could we have found guidance, were it not that Allah had guided us! [Al-A'raaf 7:43] ------>When the Quran began to be revealed, the first word of its first verse was 'Iqra' that is 'Read'. Allaah says, "Read! In the Name of your Lord Who has created (all that exists). He has created man from a clot (a piece of thick coagulated blood). Read! And your Lord is the Most Generous. Who has taught (the writing) by the pen. He has taught man that which he knew not" [Quran, 96: 1-5] ----->There is nothing which is heavier upon the balance than good character." Reported by Ahmad (6/446 and 448) ------>My Lord! Increase me in knowledge." (20/114) |